Master The Open Group OGEA-10B Exam with Reliable Practice Questions
Consider the following ADM phases objectives.
Objective
1- Determine whether an incremental approach is required, and if so identify Transition Architectures that will deliver continuous business value
2- Generate the initial complete version of the Architecture Roadmap, based upon the gap analysis and candidate Architecture Roadmap components from Phases B, C, and D
3- Finalize the Architecture Roadmap and the supporting Implementation and Migration Plan
4- Ensure that the business value and cost of work packages and Transition Architectures is understood by key stakeholders
Which phase does each objective match?
Correct : B
According to the TOGAF standard, the objectives of each ADM phase are as follows1:
* Phase E: Opportunities and Solutions
o Determine whether an incremental approach is required, and if so identify Transition Architectures that will deliver continuous business value
o Identify and group major work packages within the Architecture Roadmap
o Identify and group major implementation projects to realize the Architecture Roadmap
o Identify dependencies between increments and projects
o Estimate cost, benefit, and risk at a high level for each increment and project
o Conduct initial prioritization and sequencing of the Architecture Roadmap and projects
* Phase F: Migration Planning
o Generate the initial complete version of the Architecture Roadmap, based upon the gap analysis and candidate Architecture Roadmap components from Phases B, C, and D
o Confirm the Transition Architectures with relevant stakeholders
o Create the Implementation and Migration Plan, including Transition Architectures, work packages, projects, and other activities
o Confirm and agree the Architecture Roadmap and Implementation and Migration Plan with relevant stakeholders
* Phase G: Implementation Governance
o Finalize the Architecture Roadmap and the supporting Implementation and Migration Plan
o Ensure conformance with the Target Architecture by implementation projects
o Perform appropriate Architecture Governance functions for the solution and any implementation-driven architecture Change Requests
o Ensure that the architecture lifecycle is maintained
o Ensure that the Architecture Governance Framework is executed
* Phase H: Architecture Change Management
o Ensure that the business value and cost of work packages and Transition Architectures is understood by key stakeholders
o Manage risks and issues related to the Architecture Roadmap and Implementation and Migration Plan
o Monitor the implementation projects and Transition Architectures
o Manage changes to the architecture baseline
o Manage changes to the Architecture Capability
Therefore, the correct matching of the objectives and the phases is:
* 1G: Determine whether an incremental approach is required, and if so identify Transition Architectures that will deliver continuous business value
* 2E: Generate the initial complete version of the Architecture Roadmap, based upon the gap analysis and candidate Architecture Roadmap components from Phases B, C, and D
* 3F: Finalize the Architecture Roadmap and the supporting Implementation and Migration Plan
* 4F: Ensure that the business value and cost of work packages and Transition Architectures is understood by key stakeholders
Start a Discussions
Which of the following best summarizes the purpose of Enterprise Architecture?
Correct : B
EA applies architecture principles and practices to analyze, design, plan, and implement enterprise analysis that supports digital transformation, IT growth, and the modernization of IT2. EA also helps organizations improve the efficiency, timeliness, and reliability of business information, as well as the alignment, agility, and adaptability of the architecture to the changing needs and requirements3. Therefore, the best summary of the purpose of EA is to guide effective change.
Start a Discussions
Exhibit
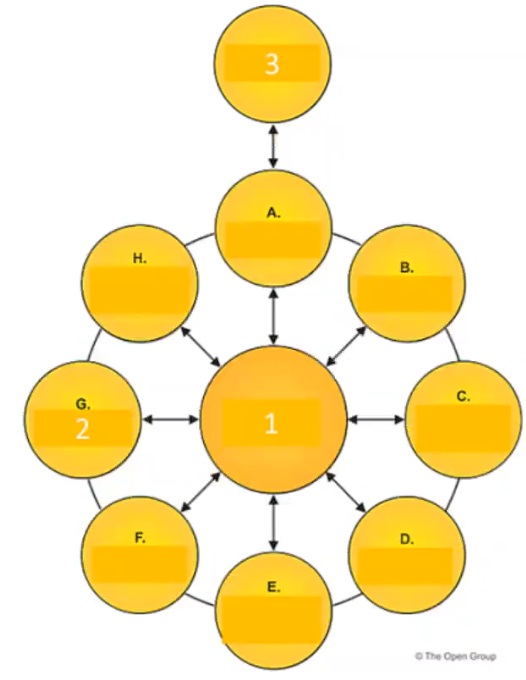
Consider the illustration showing an architecture development cycle Which description matches the phase of the ADM labeled as item 2?
Correct : D
Based on the illustration, the phase of the ADM labeled as item 2 is the Implementation Governance phase. This phase provides architectural oversight for the implementation. It ensures that the implementation project conforms to the architecture. It also provides a framework for monitoring and managing the implementation.
The Implementation Governance phase involves the following activities:
Finalizing the Architecture Roadmap and the supporting Implementation and Migration Plan
Assigning an Architecture Board to oversee the implementation
Establishing Architecture Contracts with the implementation partners
Reviewing and approving the implementation project plans and deliverables
Performing Architecture Compliance reviews to ensure alignment with the architecture
Performing Architecture Audit reviews to ensure quality and performance of the architecture
Resolving any architecture issues or change requests that arise during the implementation
Maintaining the architecture lifecycle and ensuring its continuity
The Implementation Governance phase is essential for ensuring that the architecture is realized as intended and that it delivers the expected business value and outcomes.
Start a Discussions
What are the four architecture domains that the TOGAF standard deals with?
Correct : A
The TOGAF standard divides Enterprise Architecture into four primary architecture domains: business, data, application, and technology. These domains represent different aspects of an enterprise and how they relate to each other. The business domain defines the business strategy, governance, organization, and key business processes. The data domain describes the structure of the logical and physical data assets and data management resources. The application domain provides a blueprint for the individual applications to be deployed, their interactions, and their relationships to the core business processes. The technology domain describes the logical software and hardware capabilities that are required to support the deployment of business, data, and application services. Other domains, such as motivation, security, or governance, may span across these four primary domains.Reference:
The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Core Concepts
TOGAF Standard --- Introduction - Definitions - The Open Group
The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Definitions - The Open Group
TOGAF and the history of enterprise architecture | Enable Architect
Start a Discussions
Consider the illustration.
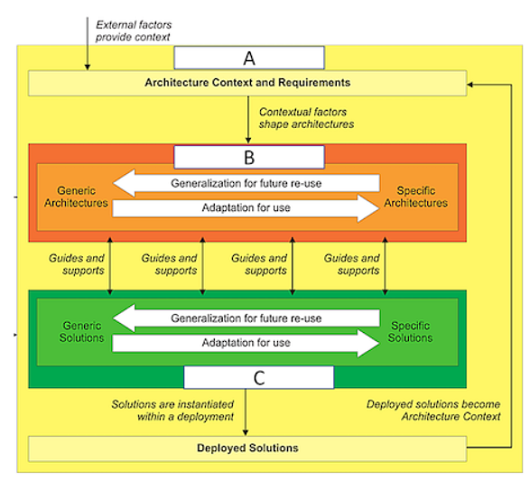
What are the items labelled A, B and C?
Correct : A
The illustration shows the relationship between the Enterprise Continuum, the Architecture Continuum, and the Solutions Continuum, which are key concepts in the TOGAF framework. The Enterprise Continuum is a view of the Architecture Repository that shows how generic foundation architectures can be leveraged and specialized to support the requirements of an individual organization. The Architecture Continuum specifies a structured classification for architectural artifacts, such as models, patterns, and descriptions, that can be reused and adapted across different domains and levels of abstraction. The Solutions Continuum identifies implemented solutions that support various stages of business and IT capability evolution, such as common systems, industry solutions, and organization-specific solutions. The illustration also shows how the architecture context and requirements are influenced by external factors, such as business drivers, stakeholders, and standards, and how they shape the generic and specific architectures and solutions. The illustration also shows how the deployed solutions become part of the architecture context for future iterations of the architecture development cycle. Reference:
* TOGAF Standard, 10th Edition, Part II: Architecture Development Method, Chapter 6: Architecture Repository, Section 6.2 Enterprise Continuum.
* TOGAF Standard, 10th Edition, Part IV: Architecture Content Framework, Chapter 35: Enterprise Continuum and Tools, Section 35.1 Introduction.
Start a Discussions