Master Salesforce MuleSoft Developer I Exam with Reliable Practice Questions
Refer to the exhibits.
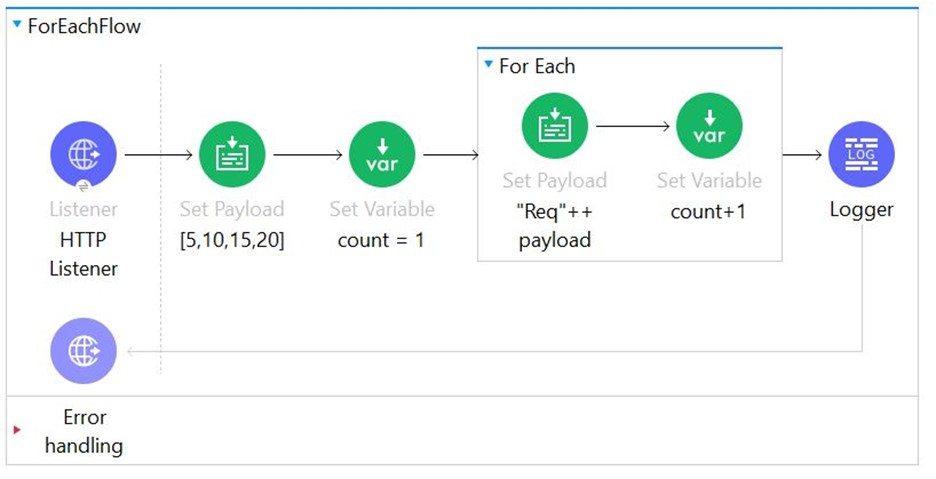
What payload and variable are logged at the end of the main flow?
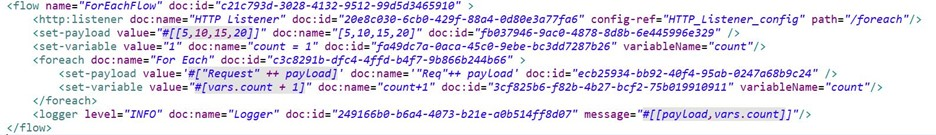
Correct : B
Correct answer is [[5, 10, 15, 20], 5]
Key thing to note here is that any changes made to payload in for each loop are not available outside for each scope where as variable value updated in for each loop is visible out side for each loop too.
In this example , sequence can be described as follows
1) Payload is set to the value [5, 10, 15, 20]
2) Variable is set to the value of 1
3) For each loop is executed four times and in each loop payload value is updated to append 'Req' and variable is count is increased by 1
4) Once control comes out of for each , payload changes made within for each are not visible. Hence payload at this point of time is equal to payload available before entering for each loop which was [5, 10, 15, 20]. Similarly variable value updated in for each loop is also available outside hence variable value is 5 as it was updated in loop.
5) Hence correct answer is [[5, 10, 15, 20], 5]
For Each Scope
The For Each scope splits a payload into elements and processes them one by one through the components that you place in the scope. It is similar to afor-each/forloop code block in most programming languages and can process any collection, including lists and arrays. The collection can be any supported content type, such asapplication/json,application/java, orapplication/xml.
General considerations about the For Each scope:
By default, For Each tries to split the payload. If the payload is a simple Java collection, the For Each scope can split it without any configuration. The payload inside the For Each scope is each of the split elements. Attributes within the original message are ignored because they are related to the entire message.
For Each does not modify the current payload. The output payload is the same as the input.
For non-Java collections, such as XML or JSON, use a DataWeave expression to split dat
a. Use theCollectionfield for this purpose.
Start a Discussions
What is output of Dataweave flatten function?
Correct : C
Correct answer is Array.
Flatten turns a set of subarrays (such as [ [1,2,3], [4,5,[6]], [], [null] ]) into a single, flattened array (such as [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, [6], null ]).
This example defines three arrays of numbers, creates another array containing those three arrays, and then uses the flatten function to convert the array of arrays into a single array with all values.
Source
%dw 2.0
output application/json
var array1 = [1,2,3]
var array2 = [4,5,6]
var array3 = [7,8,9]
var arrayOfArrays = [array1, array2, array3]
---
flatten(arrayOfArrays)
Output
[ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 ]
Start a Discussions
Refer to the exhibits. In the color flow , both the variable named color and payload are set to "red".
An HTTP POST request is then sent to the decideColor flow's HTTP Listener.
What is the payload value at the Logger component after the HTTP request completes?
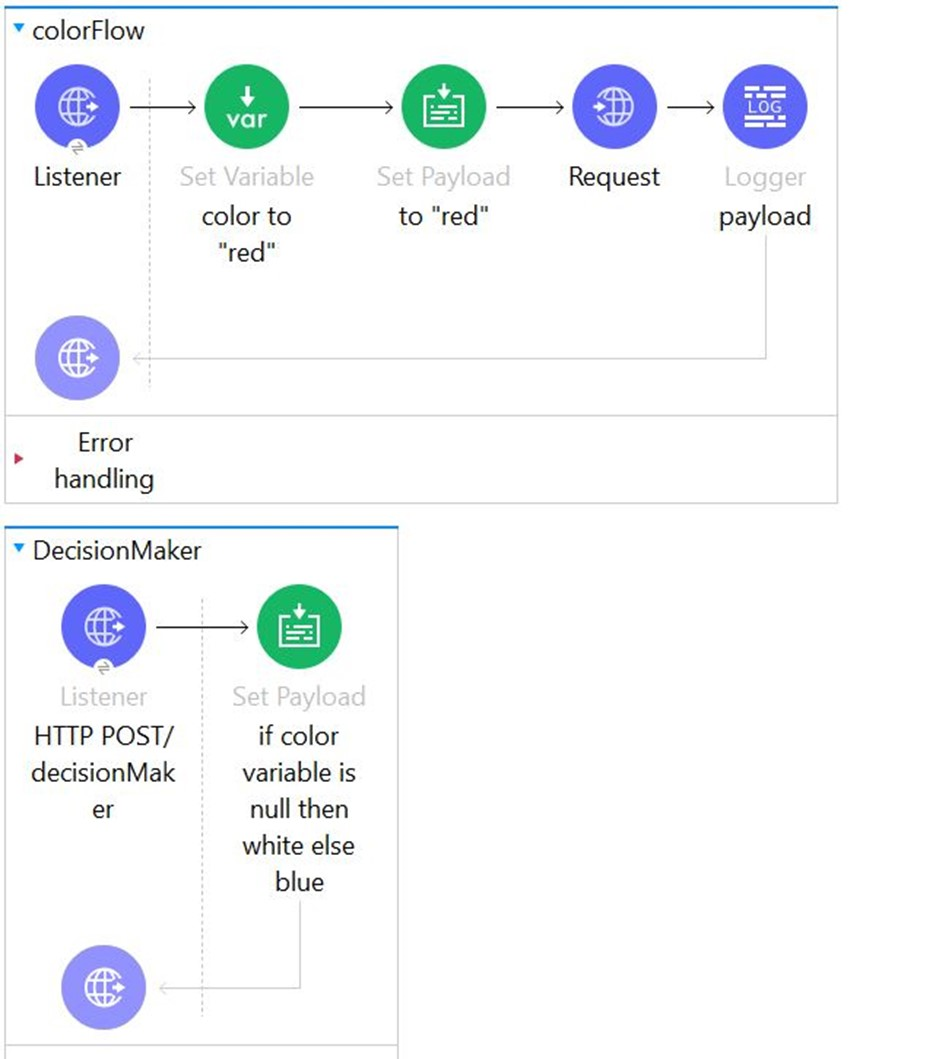
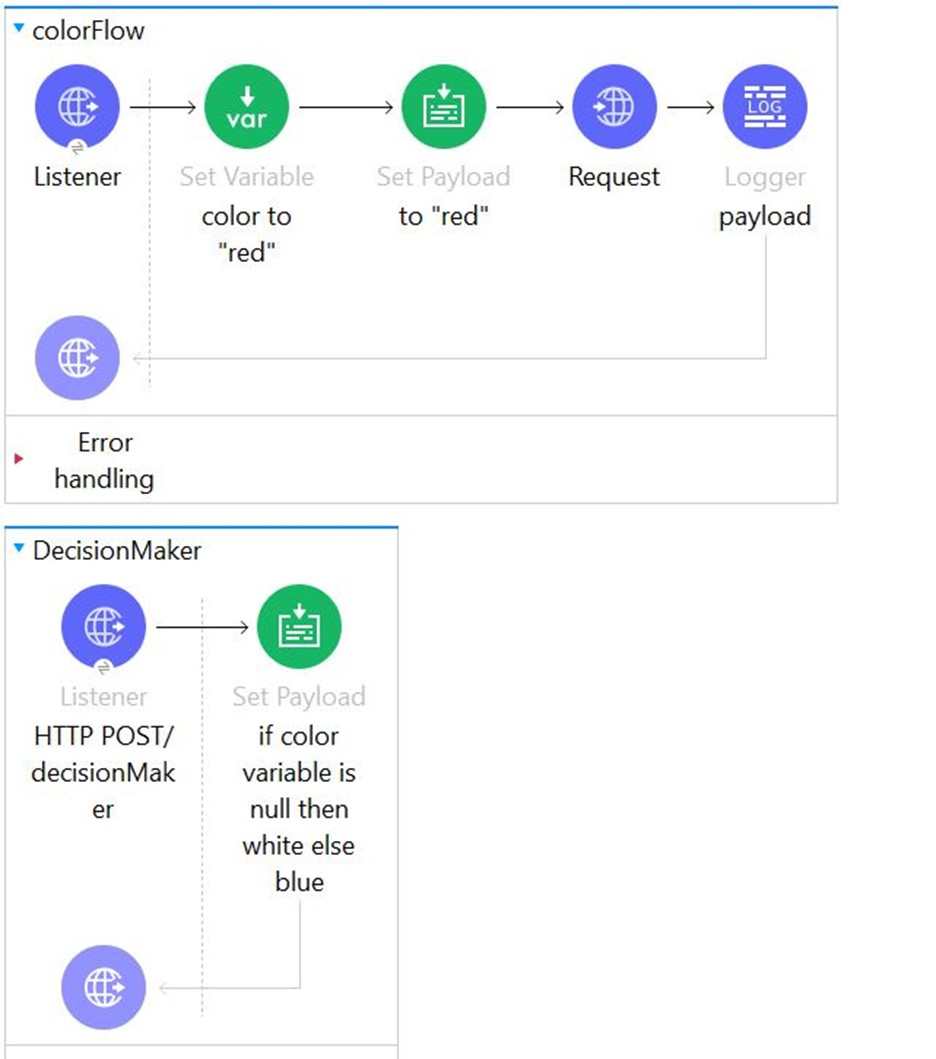
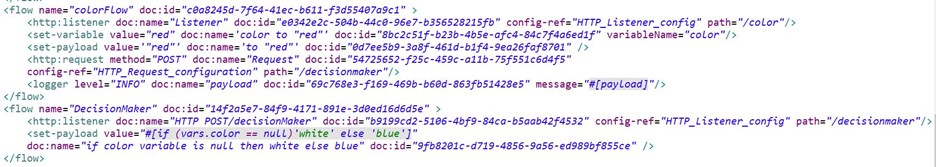
Correct : C
Start a Discussions
Refer to the exhibits. APIKit router is used to generate the flow components for RAML specification.
The Mule application must be available to REST clients using the two URL's
http://localhost:8081/internal and http://localhost:8081/external
How many APIKit Router components are generated to handle requests to every endpoint defined in RAML specification?
1. Library.raml
2. /books
3. get:
4. post:
5. /order:
6. get
7. patch
8. /members
9. get:
Correct : A
Start a Discussions
What DataWeave expression transforms the array a to the XML output?
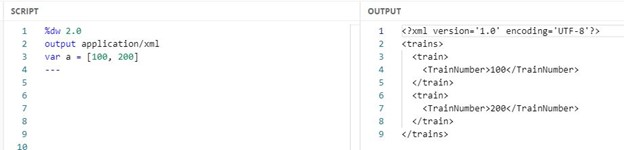
Correct : A
For such questions always look for Syntax:
I call it 'Wrap the Map'
trains:
{(
When mapping array elements (JSON or JAVA) to XML, wrap the map operations in {(..)}
-{ } are defining the object
-( ) are transforming each element in the array as a key/value pair
Start a Discussions