Master Pure Storage FAAA_004 Exam with Reliable Practice Questions
A customer is in the very early stages of designing a storage solution at a greenfield site.
They wish to use NVMe-TCP connectivity and require approximately:
* 100 Gbps of consistent raw network throughput between the FlashArray and the dedicated SAN switches.
* The dedicated SAN switches support up to 25 Gbps connectivity.
What is the minimum number of Ethernet ports in total they should connect from the FlashArray to the SAN switches while still ensuring resiliency?
Correct : A
To achieve 100 Gbps of consistent raw network throughput between the FlashArray and the dedicated SAN switches, while ensuring resiliency , the customer must connect a sufficient number of Ethernet ports from the FlashArray to the SAN switches. Given that the dedicated SAN switches support up to 25 Gbps connectivity per port , the calculation is as follows:
Throughput Requirement:
The customer requires 100 Gbps of raw throughput.
Each Ethernet port provides 25 Gbps of bandwidth.
Number of Ports Needed:
To meet the 100 Gbps requirement:

Resiliency Requirement:
Resiliency ensures that the solution can tolerate failures (e.g., switch or link failures). To achieve this, the customer must double the number of ports to provide redundant paths.
Therefore, the total number of ports required is:42=8ports.
Why Not the Other Options?
B . 2:
Two ports would only provide 50 Gbps of raw throughput (2 25 Gbps), which does not meet the 100 Gbps requirement. Additionally, there would be no redundancy, violating the resiliency requirement.
C . 4:
Four ports would meet the 100 Gbps throughput requirement but would lack redundancy, making the solution vulnerable to failures.
D . 16:
Sixteen ports would exceed the required throughput and redundancy, resulting in unnecessary costs and complexity.
Key Points:
Throughput Calculation: Ensure the total bandwidth meets the 100 Gbps requirement.
Resiliency: Double the number of ports to provide redundant paths for high availability.
Optimization: Use the minimum number of ports that satisfy both throughput and resiliency requirements.
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: 'Network Design and Configuration Best Practices'
Pure Storage Whitepaper: 'NVMe-TCP Connectivity and Performance Optimization'
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: 'Calculating Required Network Ports for FlashArray'
Start a Discussions
A potential customer has a use case where they need to use a stretched cluster for high availability and also require a third copy of their data in a remote geographic location.
Which replication method should be recommended?
Correct : D
The customer requires a storage solution that supports a stretched cluster for high availability and also maintains a third copy of their data in a remote geographic location . The best replication method to recommend is ActiveCluster with asynchronous snapshot replication .
Why This Matters:
ActiveCluster:
ActiveCluster provides synchronous replication between two sites within a stretched cluster, ensuring zero RPO and near-zero RTO for high availability.
It is ideal for scenarios where applications require continuous access to data across two locations.
Asynchronous Snapshot Replication:
Asynchronous replication extends the disaster recovery strategy by replicating snapshots to a third site. This ensures an additional layer of protection against regional failures.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . CloudSnap to an offload target:
CloudSnap is used to offload snapshots to cloud storage (e.g., AWS S3 or Azure Blob). While it satisfies the requirement for a third copy, it does not integrate with ActiveCluster for high availability in a stretched cluster.
B . Fan-out asynchronous snapshot replication:
Fan-out replication involves sending snapshots to multiple targets asynchronously. However, it does not provide the synchronous replication required for a stretched cluster.
C . ActiveDR with periodic snapshot replication:
ActiveDR is designed for asynchronous replication and failover/failback scenarios but does not support synchronous replication for a stretched cluster.
Key Points:
ActiveCluster: Ensures high availability with synchronous replication in a stretched cluster.
Async Replication: Adds a third-site replication target for comprehensive disaster recovery.
Integrated Solution: Combines high availability and disaster recovery into a single architecture.
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: 'ActiveCluster with Async Replication'
Pure Storage Whitepaper: 'Disaster Recovery Strategies with FlashArray'
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: 'Using Protection Groups in Stretched Pods'
Start a Discussions
A System Administrator has a FlashArray//X70R3. They need to add a backup element as part of their data protection strategy. They have the following requirements:
* The solution should be offsite
* Cost needs to be kept as low as possible
* The backup needs to be stored in a different location from their current FlashArray
* Restore times are not a concern
Which solution should the SE recommend to the System Administrator?
Correct : C
The System Administrator requires an offsite backup solution that is cost-effective, stores data in a different location from the current FlashArray, and does not prioritize restore times. The best solution to recommend is CloudSnap to a public cloud provider .
Why This Matters:
CloudSnap:
CloudSnap is a feature that offloads snapshots to cloud storage providers like AWS S3 or Azure Blob.
It is highly cost-effective because customers only pay for the cloud storage they use, and it eliminates the need for additional on-premises hardware.
Since restore times are not a concern, CloudSnap's slower restore process compared to on-premises solutions is acceptable.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . ActiveCluster to a FlashArray//C60:
ActiveCluster provides synchronous replication for high availability but does not meet the requirement for an offsite backup solution. Additionally, it is more expensive than CloudSnap.
B . ActiveDR to a FlashArray//C60:
ActiveDR provides asynchronous replication for disaster recovery but requires additional hardware (FlashArray//C60), which increases costs. It is less cost-effective than CloudSnap for backup purposes.
Key Points:
Cost Efficiency: CloudSnap leverages cloud storage, minimizing upfront and ongoing costs.
Offsite Storage: Ensures backups are stored in a different location from the primary FlashArray.
Restore Times: CloudSnap's slower restore process is acceptable given the customer's requirements.
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: 'CloudSnap for Offsite Backups'
Pure Storage Whitepaper: 'Cost-Effective Backup Strategies with FlashArray'
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: 'Choosing the Right Backup Solution for Your Workload'
Start a Discussions
A customer running FlashArray//X70R3 in production just purchased a FlashArray//C60R3 Array for a secondary site. The customer wants to have the lowest RPO (Recovery Point Objective) possible for the data.
Which FlashArray feature will meet the requirements?
Correct : B
The customer wants to achieve the lowest RPO (Recovery Point Objective) possible for their data when replicating between a FlashArray//X70R3 in production and a FlashArray//C60R3 at a secondary site. The best feature to meet this requirement is ActiveDR .
Why This Matters:
ActiveDR:
ActiveDR is an asynchronous replication solution designed for disaster recovery scenarios. It provides low RPOs, typically in the range of seconds to minutes , depending on network conditions and workload characteristics.
While it is asynchronous, ActiveDR achieves much lower RPOs compared to traditional async replication methods like snapshot replication.
It also supports fast failover and failback , ensuring minimal downtime during a disaster recovery event.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . ActiveCluster:
ActiveCluster provides synchronous replication with zero RPO and near-zero RTO. However, it requires both sites to be within a low-latency range (typically <10 ms). Since the customer has not specified that the secondary site is within synchronous distance, ActiveCluster is not feasible in this scenario.
C . Async Replication:
Traditional asynchronous replication (e.g., snapshot replication) typically results in higher RPOs compared to ActiveDR. It does not provide the same level of optimization for low RPOs as ActiveDR.
Key Points:
ActiveDR: Provides the lowest RPO possible for asynchronous replication, making it ideal for geographically distant secondary sites.
Network Latency: ActiveDR is designed to work efficiently over longer distances and higher latencies compared to synchronous solutions like ActiveCluster.
Disaster Recovery: Ensures protection against site failures with minimal data loss and downtime.
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: 'ActiveDR for Disaster Recovery'
Pure Storage Whitepaper: 'Meeting RPO and RTO Requirements with FlashArray'
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: 'Choosing the Right Replication Solution for High Latency'
Start a Discussions
Refer to the exhibit.
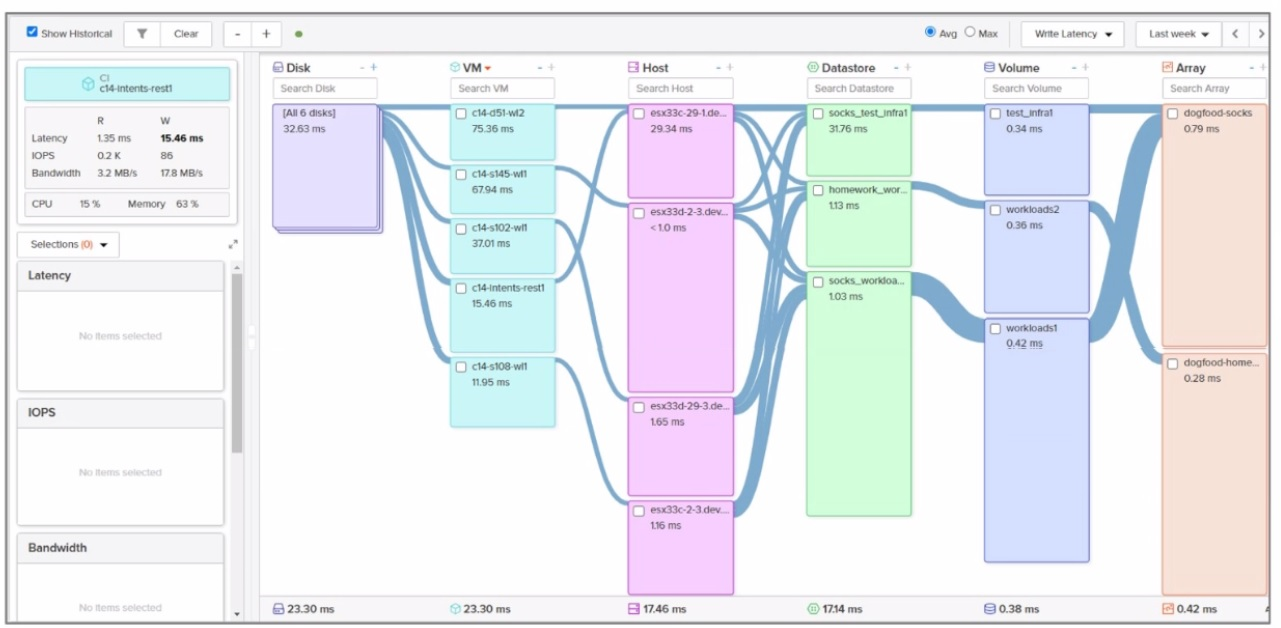
Which VM is running on the ESXi host with the lowest write latency?
Correct : A
Write Latency:
Write latency refers to the time it takes for a write operation to complete on the storage array. Lower write latency indicates better performance and faster response times for write-intensive workloads.
In Pure Storage arrays, write latency is typically measured in milliseconds (ms) and can be monitored using tools like Pure1 or Purity//FA performance metrics.
VM-to-Host Mapping:
Each VM runs on an ESXi host, and the write latency of the VM is influenced by the storage performance characteristics of the host it resides on.
To identify the VM with the lowest write latency, we must compare the write latency values for each VM listed in the exhibit.
Start a Discussions