Master iSQI CTFL_Syll2018 Exam with Reliable Practice Questions
Which of the following provides the BEST description of statement coverage?
Correct : C
Statement coverage is a white-box test technique which focuses on the percentage of executable statements that has been executed by a test suite. This is the best description of statement coverage, as it measures how many statements in the source code have been covered by one or more test cases. Option A is incorrect, as it describes state transition testing, which is a black-box test technique that uses a state table to derive test cases. Option B is incorrect, as it describes error guessing, which is an experience-based test technique in which test cases are based on the tester's knowledge of past failures. Option D is incorrect, as it describes decision coverage, which is a white-box test technique that covers the decision results which determine the next statement to be executed.
Start a Discussions
Which of the following BEST matches the descriptions with the different categories of test techniques?
1. Test cases are based on the test basis which may include the requirements, use cases and user stories
2. Test cases are based on the test basis which may include the software architecture or code
3. Test cases can show deviations from the requirements
4. These test techniques are applicable to both functional and non-functional testing
5. Tests are based on knowledge of developers, users and other stakeholders
Black - Black-box test techniques White - White-box test techniques Experience - Experience-based test techniques
Correct : D
The correct matching of the descriptions with the different categories of test techniques is as follows:
Black-box test techniques: Test cases are based on the test basis which may include the requirements, use cases and user stories (1), Test cases can show deviations from the requirements (3), These test techniques are applicable to both functional and non-functional testing (4)
White-box test techniques: Test cases are based on the test basis which may include the software architecture or code (2)
Experience-based test techniques: Tests are based on knowledge of developers, users and other stakeholders (5)
Therefore, option D is the correct answer. Options A, B, and C are incorrect, as they do not match the descriptions with the different categories of test techniques correctly.
Start a Discussions
A class grade application for instructors assigns letter grades based on students' numerical grades. The letter grades for different numerical grades should be:
Above 89. up to 100 -- A
Above 79. up to 89 - B
Above 69. up to 79 -- C
Above 59. up to 69 - D Below 60 - F
Which of the following sets of test inputs would achieve the relatively highest equivalence partition coverage?
Start a Discussions
A test score indicator for students produces a performance score based on a combination of the number of consecutive hours studied (below 4 hours. 4 to 8 hours. 9 to 12 hours or above 12 hours) and the average intensity of focus on the material during the study time (low, medium or high). Given the following test cases:

What Is the minimum number of additional test cases that are needed to ensure full coverage of all valid INPUT equivalence partitions?
Correct : C
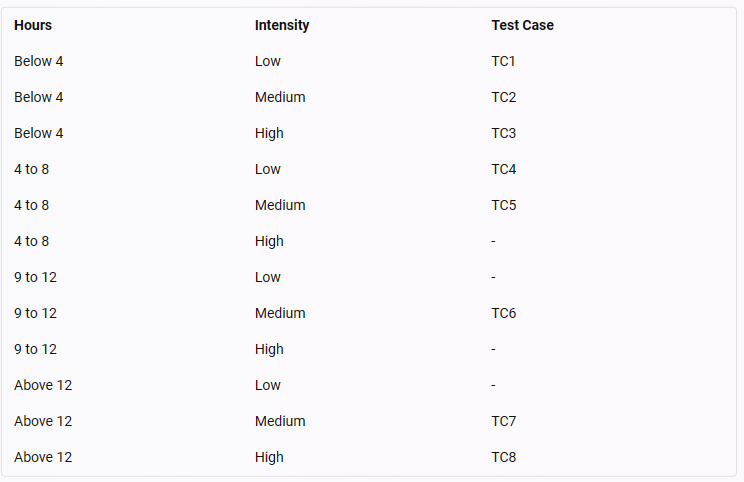
The missing partitions are marked with a dash (-). To cover these partitions, three additional test cases are needed, such as:
TC9: Hours = 4 to 8, Intensity = High
TC10: Hours = 9 to 12, Intensity = Low
TC11: Hours = 9 to 12, Intensity = High
Start a Discussions
What one of the following would be a typical objective of running a pilot project when introducing a new tool into an organisation?
Correct : D
Gaining in-depth knowledge about the tool, understanding both its strengths and weaknesses
Evaluating how the tool fits with existing processes and practices, and determining what would need to change
Assessing whether the benefits will be achieved at reasonable cost
Identifying and resolving any technical and organizational issues before deploying the tool on a larger scale
Providing training, coaching, and mentoring for users of the tool
Defining metrics to measure the success of the tool deployment
The other options are not typical objectives of running a pilot project, because they are either part of the tool selection process, or the outcomes of the pilot project. They are:
Start a Discussions