Master HPE7-A02 Exam with Reliable Practice Questions
A ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) service includes these settings:
Role Mapping Policy:
Evaluate: Select first
Rule 1 conditions:
Authorization:AD:Groups EQUALS Managers
Authentication:TEAP-Method-1-Status EQUALS Success
Rule 1 role: manager
Rule 2 conditions:
Authentication:TEAP-Method-1-Status EQUALS Success
Rule 2 role: domain-comp
Default role: [Other]
Enforcement Policy:
Evaluate: Select first
Rule 1 conditions:
Tips Role EQUALS manager AND Tips Role EQUALS domain-comp
Rule 1 profile list: domain-manager
Rule 2 conditions:
Tips Role EQUALS manager
Rule 2 profile list: manager-only
Rule 3 conditions:
Tips Role EQUALS domain-comp
Rule 3 profile list: domain-only
Default profile: [Deny access]
A client is authenticated by the service. CPPM collects attributes indicating that the user is in the Contractors group, and the client passed both TEAP methods.
Which enforcement policy will be applied?
Correct : A
1. Understanding the Role Mapping Evaluation:
Role mapping is set to 'Evaluate: Select first,' meaning the first rule that matches the client attributes will determine the role(s) assigned.
Contractors group: Since the client is in the Contractors group (not Managers), Rule 1 in the Role Mapping Policy does not match.
TEAP-Method-1-Status EQUALS Success: This condition matches Rule 2, so the client is assigned the domain-comp role.
No other rules match, so the default role [Other] is not applied.
2. Resulting Role from Role Mapping Policy:
The client is assigned the domain-comp role.
3. Enforcement Policy Evaluation:
Enforcement policy is also set to 'Evaluate: Select first,' so the first matching rule determines the enforcement profile.
Rule 1 (Tips Role = manager AND domain-comp):
The client only has the domain-comp role, not manager, so this rule does not match.
Rule 2 (Tips Role = manager):
The client does not have the manager role, so this rule does not match.
Rule 3 (Tips Role = domain-comp):
This rule matches the client's role, but it is not evaluated because the enforcement policy already skipped to the default action after failing the first two rules.
4. Default Enforcement Profile:
Since no rule explicitly matches and the policy evaluation stops at the default, the default profile [Deny Access Profile] is applied.
Final Outcome:
The client is denied access because none of the matching rules satisfy the conditions.
Reference
Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager Role Mapping and Enforcement Policies Guide.
Role and Policy Evaluation Logic for ClearPass Authentication Services.
Start a Discussions
A company has HPE Aruba Networking APs managed by HPE Aruba Networking Central. You have set up a WLAN to enforce WPA3 with 802.1X authentication.
What happens if the client fails authentication?
A. The AP assigns the client to the WLAN's default role. B. The AP drops the client because authentication aborts. C. The AP assigns the client to the WLAN's critical role. D. The AP assigns the client to the WLAN's initial role.
Correct : B
When WPA3 with 802.1X authentication is enforced on an HPE Aruba Networking WLAN, the authentication process strictly adheres to security standards. Here's how the process works:
1. 802.1X Authentication Workflow in WPA3
The client must provide valid credentials (such as certificates or username/password) to authenticate with the RADIUS server via 802.1X.
If the client fails authentication (e.g., due to invalid credentials or lack of proper configuration), the 802.1X handshake fails, and the AP terminates the connection.
2. Role Assignment in WLANs
Default Role: The role assigned to authenticated clients after a successful 802.1X authentication. It is not applied to unauthenticated clients.
Critical Role: This is a fallback role applied when there are issues communicating with the RADIUS server, not when authentication fails.
Initial Role: A temporary role assigned to clients before authentication completes. However, this role is removed once the authentication process determines failure.
3. Behavior Upon Authentication Failure
In the case of an authentication failure, the client does not get assigned to any role (default, critical, or initial) because it does not meet the conditions for network access.
The client is dropped immediately, and no further communication is allowed until reauthentication is attempted.
Explanation of Each Option
Start a Discussions
A company wants you to integrate HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) with HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Device Insight (CPDI).
What is one aspect of the integration that you should explain?
A. CPPM no longer supports any Device Profiler features and relies on CPDI for this profile information. B. CPDI must be configured as an audit server on CPPM for the integration to be successful. C. CPDI must have security analysis disabled on it for the integration to be successful. D. CPPM can submit profile information to CPDI, but if CPDI derives a different classification, CPDI takes precedence.
Correct : D
When integrating ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) with ClearPass Device Insight (CPDI), it is important to understand how device profiling and classification work between the two solutions:
1. CPPM and CPDI Integration Overview
CPPM is primarily used for access control and policy enforcement, while CPDI specializes in device profiling and classification through advanced analytics and machine learning.
Integration allows CPPM to leverage CPDI's enhanced profiling capabilities for more accurate device identification and policy enforcement.
2. Detailed Analysis of Each Option
Start a Discussions
Refer to Exhibit:
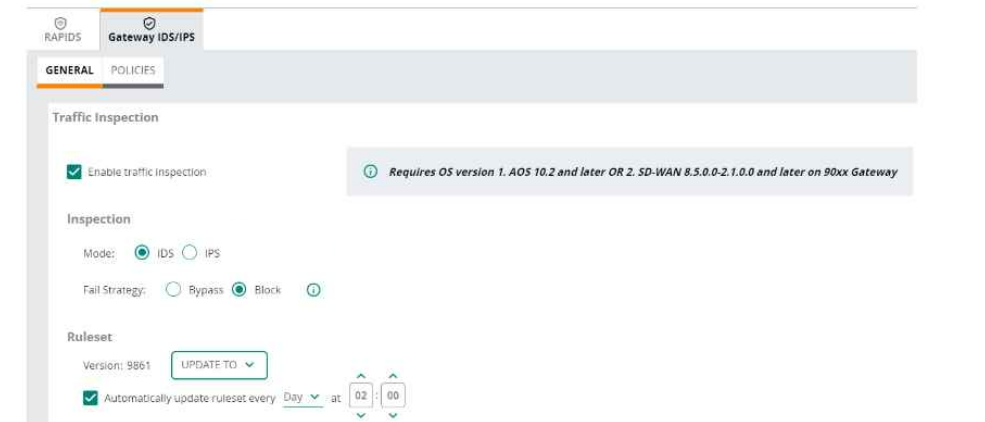
An HPE Aruba Networking 9x00 gateway is part of an HPE Aruba Networking Central group that has the settings shown in the exhibit. What would cause the gateway to drop traffic as part of its IDPS settings?
A. Its site-to-site VPN connections failing B. Traffic matching a rule in the active ruleset C. Its IDPS engine failing D. Traffic showing anomalous behavior
Correct : B
1. IDPS Mode Configuration Overview
The exhibit shows the HPE Aruba Networking Central settings for the Gateway IDS/IPS configuration:
Mode: Configured for Intrusion Prevention System (IPS), meaning that the gateway actively blocks traffic identified as threats.
Fail Strategy: Configured to Block, meaning that if the gateway cannot determine the traffic's nature due to a system issue, it will block the traffic.
Ruleset: The gateway uses a predefined set of intrusion detection/prevention rules (ruleset version 9861), which is updated automatically every day.
2. Traffic Evaluation in IPS Mode
In IPS mode, the gateway analyzes traffic against the active ruleset:
If traffic matches a rule in the ruleset and is deemed malicious, the gateway will drop the traffic as part of its prevention mechanism.
The ruleset defines specific conditions (e.g., signatures of known attacks, protocol anomalies) under which traffic should be blocked.
3. Explanation of Each Option
Start a Discussions
You are establishing a cluster of HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass servers. (Assume that they are running version 6.9.).
For which type of certificate is it recommended to install a CA-signed certificate on the Subscriber before it joins the cluster?
Correct : A
When setting up a ClearPass cluster, it is critical to ensure secure communication between the cluster nodes and the client devices. For this purpose, certain certificates must be properly configured.
1. Why HTTPS Requires a CA-Signed Certificate?
HTTPS communication is used for inter-cluster communication and for the web-based user interface that administrators use to manage the ClearPass cluster.
Before joining the cluster, it is strongly recommended to install a CA-signed HTTPS certificate on the Subscriber to ensure secure communication and prevent warnings/errors due to untrusted certificates.
Without a CA-signed certificate, the Subscriber might use a self-signed certificate, leading to security risks and lack of trust validation.
2. Analysis of Other Certificate Types
B . Database:
Incorrect: Database communications within ClearPass clusters are secured using internal certificates or keys. These are not user-facing and do not require a CA-signed certificate before joining the cluster.
C . RADIUS/EAP:
Incorrect: RADIUS/EAP certificates are important for client authentication, but they are not required on the Subscriber prior to cluster joining. These can be configured after the Subscriber is part of the cluster.
D . RadSec:
Incorrect: RadSec is an optional feature for secure RADIUS communication over TLS, and its certificate configuration is typically performed post-cluster setup.
Final Recommendation
To ensure secure cluster operations and seamless web-based management, a CA-signed HTTPS certificate should be installed on the Subscriber before it joins the ClearPass cluster.
Reference
ClearPass Deployment Guide for Version 6.9.
Best Practices for Certificate Management in ClearPass Clusters.
HPE Aruba ClearPass Cluster Configuration Guide.
Start a Discussions