Master HashiCorp HCVA0-003 Exam with Reliable Practice Questions
What can be used to limit the scope of a credential breach?
Correct : C
Using a short-lived dynamic secrets can help limit the scope of a credential breach by reducing the exposure time of the secrets. Dynamic secrets are generated on-demand by Vault and automatically revoked when they are no longer needed. This way, the credentials are not stored in plain text or in a static database, and they can be rotated frequently to prevent unauthorized access. Dynamic secrets also provide encryption as a service, which means that they perform cryptographic operations on data in-transit without storing any data. This adds an extra layer of security and reduces the risk of data leakage or tampering. Reference: Dynamic secrets | Vault | HashiCorp Developer, What are dynamic secrets and why do I need them? - HashiCorp
Start a Discussions
What environment variable overrides the CLI's default Vault server address?
Correct : B
The environment variable VAULT_ADDR overrides the CLI's default Vault server address. The VAULT_ADDR environment variable specifies the address of the Vault server that is used to communicate with Vault from other applications or processes. By setting this variable, you can avoid hard-coding the Vault server address in your code or configuration files, and you can also use different addresses for different environments or scenarios. For example, you can use a local development server for testing purposes, and a production server for deploying your application. Reference: Commands (CLI) | Vault | HashiCorp Developer, Vault Agent - secrets as environment variables | Vault | HashiCorp Developer
Start a Discussions
Which of the following statements describe the CLI command below?
S vault login -method-1dap username-mitche11h
Correct : A
The CLI command vault login -method ldap username=mitchellh generates a token that is response wrapped. This means that the token contains a base64-encoded response wrapper, which is a JSON object that contains information about the token, such as its policies, metadata, and expiration time. The response wrapper is used to verify the authenticity and integrity of the token, and to prevent replay attacks. The response wrapper also allows Vault to automatically renew the token when it expires, or to revoke it if it is compromised. The -method ldap option specifies that the authentication method is LDAP, which requires a username and password to be provided. The username mitchellh is an example of an LDAP user name, and the password will be hidden when entered. Reference: Vault CLI Reference | Vault | HashiCorp Developer, Vault CLI Reference | Vault | HashiCorp Developer
Start a Discussions
The following three policies exist in Vault. What do these policies allow an organization to do?
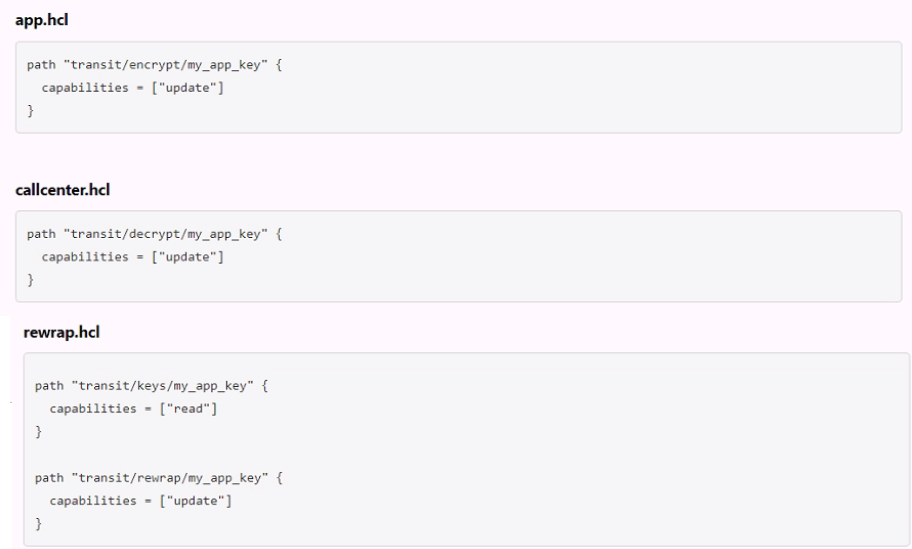
Correct : C
The three policies that exist in Vault are:
admins: This policy grants full access to all secrets and operations in Vault. It can be used by administrators or operators who need to manage all aspects of Vault.
default: This policy grants access to all secrets and operations in Vault except for those that require specific policies. It can be used as a fallback policy when no other policy matches.
transit: This policy grants access only to the transit secrets engine, which handles cryptographic functions on data in-transit. It can be used by applications or services that need to encrypt or decrypt data using Vault.
These policies allow an organization to perform useful tasks such as:
Encrypting, decrypting, and rewrapping data using the transit engine all in one policy: This policy grants access to both the transit secrets engine and the default policy, which allows performing any operation on any secret in Vault.
Creating a transit encryption key for encrypting, decrypting, and rewrapping encrypted data: This policy grants access only to the transit secrets engine and its associated keys, which are used for encrypting and decrypting data in transit using AES-GCM with a 256-bit AES key or other supported key types.
Separating permissions allowed on actions associated with the transit secret engine: This policy grants access only to specific actions related to the transit secrets engine, such as creating keys or wrapping requests. It does not grant access to other operations or secrets in Vault.
Start a Discussions
Your DevOps team would like to provision VMs in GCP via a CICD pipeline. They would like to integrate Vault to protect the credentials used by the tool. Which secrets engine would you recommend?
Correct : A
The Google Cloud Secrets Engine is the best option for the DevOps team to provision VMs in GCP via a CICD pipeline and integrate Vault to protect the credentials used by the tool. The Google Cloud Secrets Engine can dynamically generate GCP service account keys or OAuth tokens based on IAM policies, which can be used to authenticate and authorize the CICD tool to access GCP resources. The credentials are automatically revoked when they are no longer used or when the lease expires, ensuring that the credentials are short-lived and secure. The DevOps team can configure rolesets or static accounts in Vault to define the scope and permissions of the credentials, and use the Vault API or CLI to request credentials on demand. The Google Cloud Secrets Engine also supports generating access tokens for impersonated service accounts, which can be useful for delegating access to other service accounts without storing or managing their keys1.
The Identity Secrets Engine is not a good option for this use case, because it does not generate GCP credentials, but rather generates identity tokens that can be used to access other Vault secrets engines or namespaces2. The Key/Value Secrets Engine version 2 is also not a good option, because it does not generate dynamic credentials, but rather stores and manages static secrets that the user provides3. The SSH Secrets Engine is not a good option either, because it does not generate GCP credentials, but rather generates SSH keys or OTPs that can be used to access remote hosts via SSH4.
Google Cloud - Secrets Engines | Vault | HashiCorp Developer
Identity - Secrets Engines | Vault | HashiCorp Developer
KV - Secrets Engines | Vault | HashiCorp Developer
SSH - Secrets Engines | Vault | HashiCorp Developer
Start a Discussions