Master CIPS L6M2 Exam with Reliable Practice Questions
SIMULATION
Examine how an organisation can strategically position itself within the marketplace.
Correct : A
How an Organization Can Strategically Position Itself in the Marketplace
Strategic positioning is the process by which an organization differentiates itself from competitors and establishes a strong, sustainable presence in the market. It involves making key decisions regarding branding, pricing, customer engagement, and competitive advantage to attract and retain customers.
Below are the key strategies an organization can use to position itself strategically in the marketplace:
1. Competitive Strategy (Porter's Generic Strategies)
Organizations can use Michael Porter's Competitive Strategies to define their market position:
Cost Leadership -- Competing on price by offering the lowest-cost products or services.
Differentiation -- Offering unique, high-quality, or innovative products that stand out.
Focus (Niche Strategy) -- Targeting a specific market segment with specialized products or services.
Example:
Aldi (Cost Leadership) keeps prices low by optimizing supply chains.
Apple (Differentiation) uses innovation and brand exclusivity to dominate the premium tech market.
Rolls-Royce (Focus Strategy) targets a niche luxury segment instead of mass markets.
2. Strong Branding and Market Perception
Organizations must build a strong brand identity to differentiate themselves. This includes:
Consistent Branding -- Using logos, colors, and messaging that reinforce identity.
Emotional Connection -- Telling a brand story that resonates with customers.
Trust and Reputation -- Delivering quality products and services to establish credibility.
Example:
Coca-Cola uses global branding to evoke happiness and refreshment, maintaining strong market dominance.
Tesla markets itself as an innovative, eco-friendly brand, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
3. Innovation and Product Development
To maintain a competitive edge, companies must invest in innovation and continuously improve their products/services.
Technology Adoption -- Implementing cutting-edge solutions (e.g., AI, automation).
Customer-Centric Innovation -- Developing products based on customer needs.
First-Mover Advantage -- Being the first to introduce groundbreaking products.
Example:
Amazon's AI-driven supply chain ensures fast deliveries and high customer satisfaction.
Netflix's streaming model revolutionized entertainment consumption, making it an industry leader.
4. Digital Transformation and Market Reach
Organizations can use digital tools and platforms to enhance their strategic positioning:
E-commerce & Online Presence -- Expanding reach beyond physical locations.
Social Media & Influencer Marketing -- Engaging with customers through digital channels.
Data Analytics -- Using customer insights to make strategic decisions.
Example:
Nike's e-commerce growth and direct-to-consumer (DTC) model strengthened its competitive position.
Zara's fast fashion strategy, driven by data analytics, allows quick response to trends.
5. Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Modern consumers prefer brands that demonstrate social and environmental responsibility. Companies can differentiate themselves by:
Sustainable Sourcing -- Using eco-friendly materials and ethical suppliers.
Corporate Ethics -- Promoting fair labor practices and social initiatives.
Carbon Footprint Reduction -- Committing to green energy and carbon neutrality.
Example:
Patagonia's sustainability-first strategy attracts eco-conscious consumers.
Unilever's ''Sustainable Living Plan'' enhances brand loyalty through ethical business practices.
6. Strategic Partnerships and Market Expansion
Organizations can strengthen their market position through collaborations and global expansion:
Mergers & Acquisitions -- Gaining market share by acquiring competitors.
Joint Ventures -- Partnering with companies for mutual growth.
New Market Entry -- Expanding into emerging markets.
Example:
Google acquiring YouTube enhanced its presence in digital content.
Starbucks' partnership with Nestl expanded its global coffee distribution.
Conclusion
Strategic positioning requires a clear understanding of competitive advantage, market needs, and innovative growth strategies. By leveraging cost leadership, differentiation, branding, innovation, digital transformation, sustainability, and partnerships, organizations can sustain long-term success in a competitive market.
Start a Discussions
SIMULATION
Explain how culture and historic influences can impact upon a business's strategic decisions and positioning within the marketplace
Correct : A
How Culture and Historic Influences Impact Strategic Decisions and Market Positioning
A business's strategic decisions and positioning within the marketplace are shaped by both organizational culture and historical influences. These factors affect how a company develops strategy, interacts with customers, manages employees, and competes globally.
1. The Role of Organizational Culture in Strategic Decisions
Organizational culture is the shared values, beliefs, and behaviors within a company. It influences decision-making, innovation, and competitive advantage.
How Culture Affects Strategy
Risk Appetite -- A culture that embraces innovation (e.g., Google) will invest in R&D, while risk-averse cultures (e.g., traditional banks) focus on stability.
Decision-Making Speed -- Hierarchical cultures (e.g., Japanese firms) rely on consensus, while Western firms (e.g., Apple) may have centralized decision-making.
Customer Engagement -- A customer-centric culture (e.g., Amazon) leads to investment in personalization and AI-driven recommendations.
Example:
Toyota's Kaizen Culture (Continuous Improvement) has shaped its lean manufacturing strategy, giving it a competitive advantage in cost efficiency.
2. How Historic Influences Shape Business Strategy
Historical events, past business performance, economic trends, and industry evolution shape how businesses position themselves in the marketplace.
How History Affects Strategy
Legacy of Innovation or Conservatism -- Companies with a history of innovation (e.g., IBM, Tesla) continuously push boundaries, while firms with traditional roots (e.g., British banks) focus on risk management.
Economic Crises and Financial Stability -- Businesses that survived financial crises (e.g., 2008 recession) tend to develop risk-averse financial strategies.
Market Reputation and Consumer Perception -- A strong historical reputation can be leveraged for branding (e.g., Rolls-Royce's luxury image).
Example:
Lego nearly went bankrupt in the early 2000s, leading it to redefine its strategy, focus on digital gaming partnerships, and revive its brand.
3. The Influence of National and Corporate Culture on Global Positioning
When expanding globally, businesses must align their strategies with different cultural expectations.
How Culture Affects Global Market Entry
Consumer Preferences -- Fast food chains adapt menus for local cultures (e.g., McDonald's in India offers vegetarian options).
Negotiation & Communication Styles -- Business negotiations in China emphasize relationships ('Guanxi'), while Western firms prioritize efficiency.
Leadership and Management Approaches -- German firms emphasize engineering precision, while Silicon Valley firms prioritize agility and experimentation.
Example:
IKEA modifies store layouts in different countries---small apartments in Japan vs. large home spaces in the U.S.
4. Strategic Positioning Based on Cultural & Historic Factors
A company's historical and cultural influences define its positioning strategy:
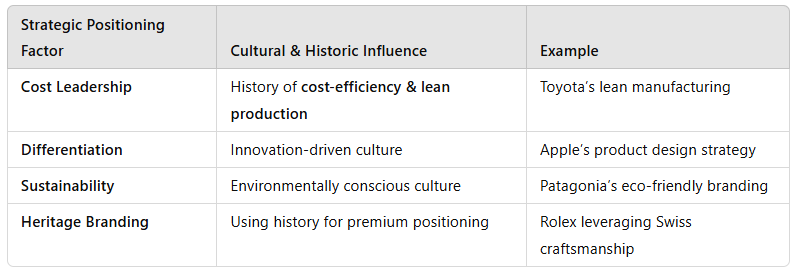
Conclusion
A business's strategic decisions and market positioning are deeply influenced by organizational culture, national culture, and historical performance. Companies that leverage their cultural strengths and adapt to market history can achieve long-term competitive advantage.
Start a Discussions
SIMULATION
XYZ is a construction firm which builds houses in Birmingham. Discuss a tool that it can use to assess the remote environment and discuss a tool it can use to evaluate the operating environment.
Correct : A
Environmental Analysis Tools for XYZ Construction Firm
To make strategic decisions, XYZ Construction needs to assess both the remote environment (external macro factors) and the operating environment (industry-specific and competitive factors). Two widely used tools for these assessments are:
PESTLE Analysis -- for analyzing the remote environment
Porter's Five Forces -- for evaluating the operating environment
1. Assessing the Remote Environment: PESTLE Analysis
Tool: PESTLE Analysis helps organizations evaluate macro-environmental factors that impact long-term business strategy.
Why use PESTLE?
It identifies external influences (political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental) that XYZ cannot control but must respond to.
PESTLE Analysis for XYZ Construction:

Example: If the UK government introduces new housing grants, XYZ may expand operations to capitalize on increased demand.
2. Evaluating the Operating Environment: Porter's Five Forces
Tool: Porter's Five Forces helps XYZ analyze industry-specific competition and market dynamics.
Why use Porter's Five Forces?
It helps assess competitive pressures that impact XYZ's profitability and positioning.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis for XYZ Construction:
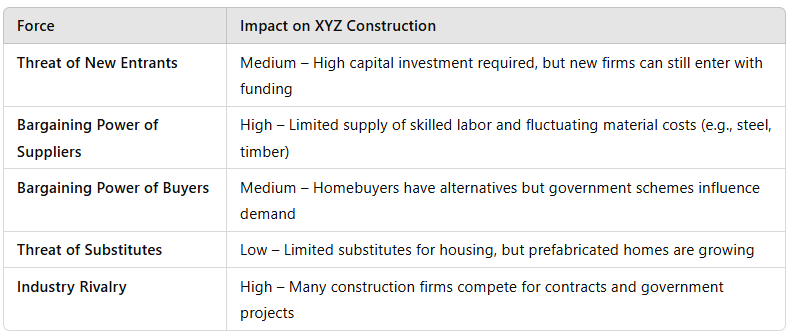
Example: If supplier power is high due to rising material costs, XYZ must negotiate better contracts or explore alternative suppliers.
Conclusion
PESTLE Analysis helps XYZ understand the external environment affecting the construction industry.
Porter's Five Forces enables XYZ to evaluate industry competition and make informed strategic choices.
Start a Discussions
SIMULATION
Describe and evaluate the use of the VRIO Framework in understanding the internal resources and competencies of an organisation.
Correct : A
The VRIO Framework: Understanding Internal Resources and Competencies
The VRIO Framework is a strategic analysis tool used to assess an organization's internal resources and competencies to determine whether they provide a sustainable competitive advantage. Developed by Jay Barney, VRIO stands for Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organization.
1. Explanation of the VRIO Framework
The VRIO model evaluates whether a firm's resources and capabilities contribute to a sustained competitive advantage.
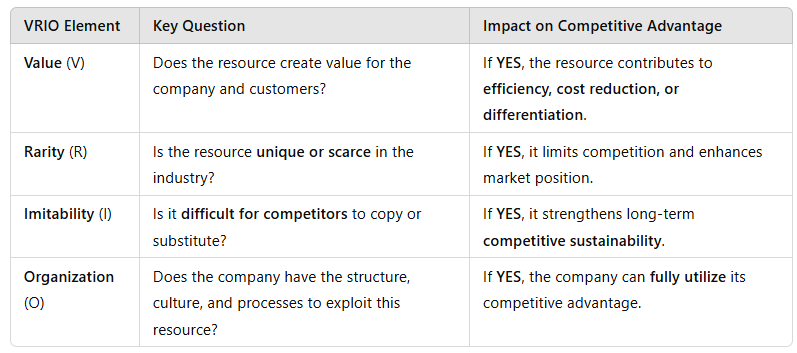
Example: Apple's software ecosystem (iOS, App Store) is valuable, rare, hard to imitate, and well-organized, giving it a sustainable competitive advantage.
2. The Use of VRIO in Assessing Internal Resources and Competencies
Companies use the VRIO framework to identify which resources provide temporary or sustainable competitive advantages.
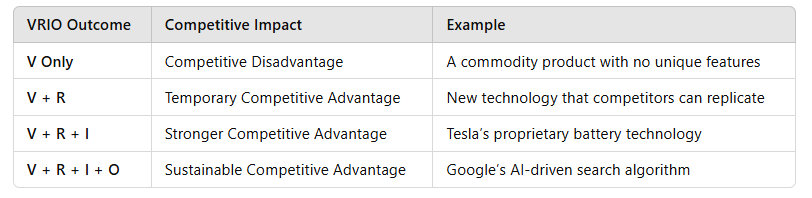
3. Advantages of Using VRIO in Strategic Decision-Making
Identifies Core Competencies -- Helps organizations focus on key strengths that drive long-term success.
Guides Investment Decisions -- Encourages businesses to invest in resources that are difficult to imitate.
Improves Competitive Strategy -- Helps firms differentiate between short-term vs. long-term advantages.
Example: Coca-Cola's brand equity is VRIO-positive, making it difficult for new entrants to replicate.
4. Limitations of the VRIO Framework
Ignores External Factors -- Unlike PESTLE or Porter's Five Forces, VRIO does not account for market conditions or regulatory changes.
Subjectivity in Resource Evaluation -- Assessing whether a resource is truly valuable or rare can be complex.
Lack of Actionable Steps -- VRIO identifies competitive strengths but does not provide strategies for leveraging them.
Example: A company may identify a rare talent pool, but poor organizational structure (O) can prevent it from leveraging this advantage.
5. Application of VRIO in Business Strategy
Businesses across different industries use VRIO to assess their internal strengths:
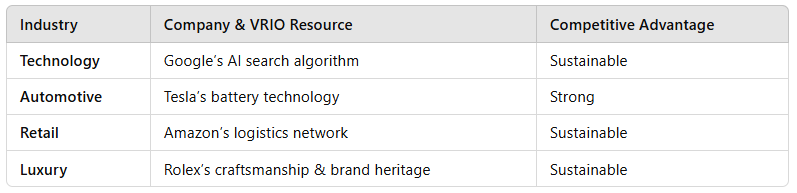
Conclusion
The VRIO Framework is a valuable tool for evaluating internal resources and capabilities, allowing businesses to identify sustainable competitive advantages. However, it should be used alongside external analysis tools (e.g., PESTLE, SWOT) to ensure a comprehensive strategic assessment.
Start a Discussions
SIMULATION
Discuss how XYZ, a global beverage manufacturing organisation, could use the Boston Consultancy Group Framework to impact upon strategic decision making
Introduction
The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix is a strategic tool used by organizations to analyze their product portfolio and allocate resources effectively. It classifies products into four categories---Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs---based on market growth rate and market share.
As a global beverage manufacturing organization, XYZ can use the BCG Matrix to evaluate its product range, identify growth opportunities, and make informed strategic decisions.
1. Explanation of the BCG Matrix
The BCG Matrix is divided into four quadrants:
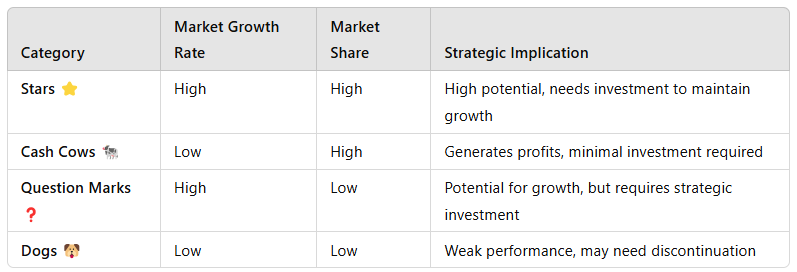
Example for XYZ:
Star: A fast-growing energy drink brand in emerging markets.
Cash Cow: A flagship cola product with stable market demand.
Question Mark: A new functional health drink with uncertain market acceptance.
Dog: An underperforming diet soda variant with declining sales.
2. How XYZ Can Use the BCG Matrix for Strategic Decision-Making
XYZ can use the BCG Matrix to make resource allocation and investment decisions based on product performance.

3. Advantages of Using the BCG Matrix for XYZ
Resource Allocation -- Helps prioritize investment in high-growth products.
Strategic Focus -- Identifies which products to grow, maintain, or phase out.
Market Adaptation -- Helps XYZ adjust its beverage portfolio based on changing consumer trends.
Example: If XYZ's energy drink (a Star) is experiencing high growth, more marketing and production investment may be justified.
4. Limitations of the BCG Matrix
Ignores Market Competition -- A product may have a high market share, but competition could still impact profitability.
Simplistic Assumptions -- Not all products neatly fit into one category; market dynamics are complex.
Focuses on Growth and Share Only -- It does not consider external factors like profit margins, customer loyalty, or brand strength.
Example: A Question Mark product might have potential, but if consumer preferences shift, it may never become a Star.
5. Application of the BCG Matrix in the Beverage Industry
XYZ can apply the BCG Matrix by reviewing its entire product portfolio across different geographic markets.

Conclusion
The BCG Matrix is a valuable strategic tool for XYZ to analyze its product portfolio, prioritize investments, and make informed market-based decisions. However, it should be used alongside other strategic models (e.g., PESTLE, VRIO) to ensure a comprehensive business strategy.
Correct : A
Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix and Strategic Decision-Making for XYZ
Start a Discussions