Master CIDQ IDFX Exam with Reliable Practice Questions
If budget is the primary criterion, which method of veneer matching within individual panel faces is best?
A. Balance match B. Running match C. Blueprint matched D. Balance and center match
Explanation: Veneer matching refers to the method used to arrange wood veneer leaves on a panel to achieve a desired aesthetic effect. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and standards from the Architectural Woodwork Institute (AWI) and the Woodwork Institute (WI) outline different veneer matching techniques, each with varying levels of cost and complexity. When budget is the primary criterion, the method that minimizes waste and labor is preferred.
Correct : B
NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual, Chapter 7: Design Elements and Principles.
Architectural Woodwork Standards (AWS), Section 4: Veneer Matching.
Start a Discussions
The most appropriate scale for a millwork elevation drawing is
A. 1/32" [0.79 mm] B. 1/16" [1.59 mm] C. 1/8" [3.12 mm] D. 1/2" [12.7 mm]
Explanation: Millwork elevation drawings show detailed views of custom woodwork, such as cabinetry, trim, or paneling, and require a scale that provides enough detail for accurate fabrication and installation. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and standard drafting practices (e.g., as outlined by the Architectural Woodwork Institute [AWI] and the National CAD Standard [NCS]) specify appropriate scales for different types of drawings based on their level of detail.
Correct : D
NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual, Chapter 5: Construction Drawings and Specifications.
Architectural Woodwork Standards (AWS), Section 1: Architectural Woodwork Drawings.
Start a Discussions
Which sink is accessible in a corporate break room?
Correct : A
For a sink to be accessible in a corporate break room, it must comply with ADA standards, which include a maximum height of 34 inches (864 mm) above the finished floor, a clear floor space for approach, and knee space for wheelchair users. Additionally, exposed pipes must be insulated to prevent burns. Option A (integral solid surface sink at 34' H with a 30' x 48' front approach and insulated piping) meets all requirements: the height is correct, the front approach space is adequate, and the piping is insulated. Option B (undermount stainless steel sink with a side approach) has a 30' x 42' approach, which is too narrow for a side approach (ADA requires 30' x 48'), and a grab bar is not required for a sink. Option C (porcelain drop-in sink with exposed rim) may pose a barrier due to the rim, which can obstruct access for wheelchair users, despite meeting other criteria.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on accessibility standards.
Exact Extract: The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual references ADA standards, stating, ''An accessible sink must be no higher than 34 inches (864 mm), provide a 30' x 48' front approach, and have insulated piping to protect wheelchair users.''
Objectives:
Apply accessibility standards to break room design (IDFX Objective: Codes and Standards).
Design accessible fixtures for public spaces (IDFX Objective: Human Behavior and the Designed Environment).
NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Section on Accessibility).
ADA Standards for Accessible Design (Section 606: Lavatories and Sinks).
Start a Discussions
What is the MOST appropriate way to determine the number of lavatories required in a commercial restroom [washroom]?
Correct : C
The number of lavatories required in a commercial restroom is determined by plumbing codes, which are based on the building's occupancy type and occupant load. The International Plumbing Code (IPC) or local plumbing codes specify the minimum number of fixtures (e.g., lavatories, toilets) required per occupant load, ensuring adequate facilities for hygiene and safety. Consulting the plumbing code based on the building's jurisdiction is the most appropriate method, as it provides a legally binding standard. Option A (interview the client) may provide user data but does not ensure code compliance. Option B (create a floor plan) determines space availability, not the required number of fixtures.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on plumbing codes.
Exact Extract: The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual states, ''The number of lavatories in a commercial restroom must be determined by consulting the plumbing code based on the building's jurisdiction, which specifies fixture requirements by occupancy and load.''
Objectives:
Apply plumbing codes to restroom design (IDFX Objective: Codes and Standards).
Ensure adequate facilities in commercial spaces (IDFX Objective: Design Application).
NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Section on Codes and Standards).
International Plumbing Code (IPC), Section 403: Minimum Plumbing Facilities.
Start a Discussions
Which dimension does not meet accessibility standards?
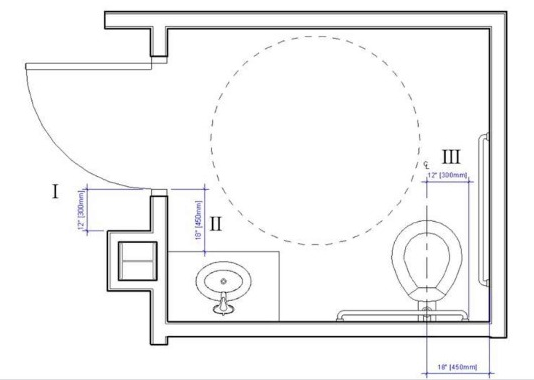
Correct : A
Accessibility standards, such as those outlined in the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) Standards for Accessible Design and ANSI A117.1, are critical in ensuring that spaces like bathrooms are usable by individuals with disabilities. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual incorporates these standards, providing guidelines for clearances, fixture heights, and other accessibility requirements.
Let's evaluate the dimensions in the image:
Dimension I: 12 inches [300 mm]: This dimension represents the clearance between the edge of the door and the adjacent wall or fixture (likely the sink). ADA Section 404.2.4.3 requires a minimum clearance on the pull side of a door for a front approach. For a front approach on the pull side, a minimum of 18 inches (457 mm) of clearance is required beside the door (on the latch side) to allow a wheelchair user to maneuver and open the door. A 12-inch (300 mm) clearance is insufficient, making this dimension non-compliant with accessibility standards.
Dimension II: 18 inches [450 mm]: This is the clearance between the centerline of the toilet and the edge of the sink. ADA Section 604.3.2 requires a minimum of 18 inches (457 mm) from the centerline of the toilet to the nearest obstruction for a side approach, which this dimension meets (though it is slightly below 457 mm, it is typically rounded to 18 inches in practice).
Dimension III: 17 inches [425 mm]: This is the height of the toilet seat from the floor. ADA Section 604.4 requires the toilet seat height to be between 17 inches (430 mm) and 19 inches (485 mm) above the finished floor, which this dimension meets.
Dimension IV: 18 inches [450 mm]: This is the clearance between the centerline of the toilet and the wall. ADA Section 604.3.1 requires a minimum of 18 inches (457 mm) from the centerline of the toilet to the nearest wall for a side approach, which this dimension meets.
Dimension I (12 inches or 300 mm) does not meet the ADA requirement for door maneuvering clearance, making it the dimension that fails to comply with accessibility standards.
Verified Answer from Official Source: The correct answer is A, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and ADA Standards for Accessible Design.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 2: Building Codes and Standards): 'Accessibility standards require a minimum of 18 inches (457 mm) of clearance on the pull side of a door for a front approach to ensure proper maneuvering space for wheelchair users.'
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that accessibility standards, such as the ADA, require a minimum of 18 inches of clearance on the pull side of a door for a front approach to accommodate wheelchair users. Dimension I (12 inches) falls short of this requirement, making it non-compliant and the dimension that needs to be changed to meet accessibility standards.
Objectives:
Understand accessibility requirements for door maneuvering clearances in bathrooms.
Apply ADA standards to ensure spaces are accessible for individuals with disabilities.
NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual, Chapter 2: Building Codes and Standards.
ADA Standards for Accessible Design, Section 404: Doors, Doorways, and Gates.
Start a Discussions